Range of Motion in Exercise
Author name
The human body is an amazing machine.
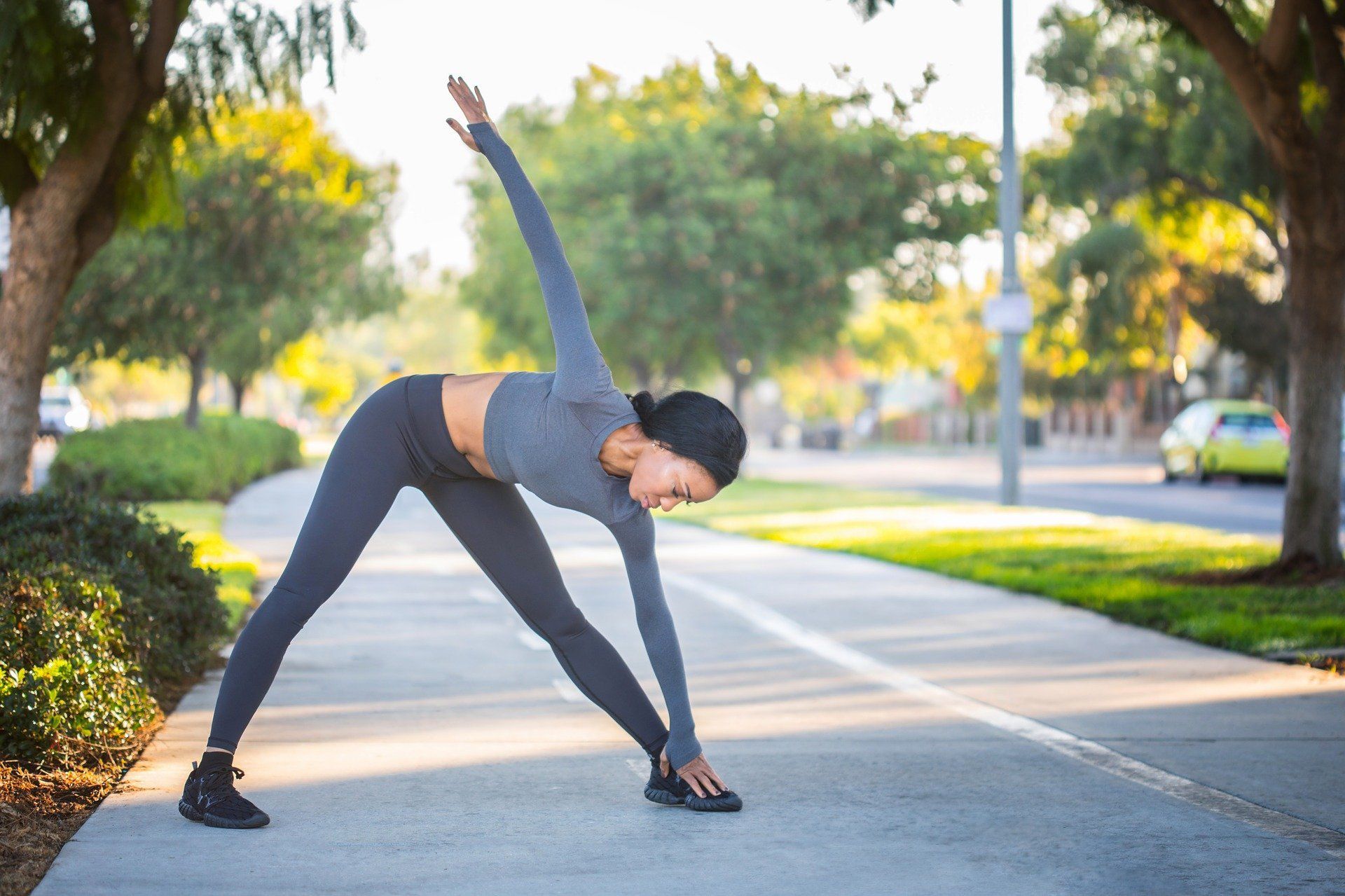

Bones, joints and muscle work together in unison to help the body move. These elements are what is needed to allow the body to walk, run, jump, push and pull. The joint, or articulation, is where two bones come together. The flexion and extension, or bending at the joint, is what is referred to as Range of Motion. A healthy Range of Motion is important for a robust quality of life. The tighter one’s Range Of Motion is during everyday movement, the more difficult it becomes to perform normal daily tasks.
The body is meant to move. Joints are meant to allow the body to get into positions that serve a purpose. Range of Motion or ROM, is influenced by numerous structures: configuration of bone surfaces within the joint, joint capsule, ligaments, tendons, and muscles moving about the joint. Overuse of major muscles and prolonged sitting can attribute to a decrease in joint mobility.
Range of Motion (ROM) exercise refers to activity aimed at improving movement of specific joints.
There are three types of ROM exercises; Passive, Active and Active Assistive.
Passive ROM is when the movement applied to a joint by another person or by a passive motion machine. When passive ROM is applied, the joint is completely relaxed while the outside force moves the body part throughout the obtainable range.
Active ROM is movement of a joint by the person performing the exercise. Examples would include a person performing a static hold stretch for any period of time or a runner preparing for a race by performing “butt-kicks” and “high-knee” stretches before the event.
Active Assist ROM is when a joint is receiving partial assistance from an outside force. This range of motion may result from the motion applied by the exerciser or by the person assisting the individual. It also may be a half-and-half effort on the joint from each source. A great example of this is when exercisers practice Partner Yoga or when gymnasts perform face to face splits, join hands and take turns laying back while holding that leg stretch.
Of course, injury, surgery, or immobilization of a joint may affect the normal joint range of motion. Motion may also be limited because of a problem within the joint, pain, swelling in the area of the joint, or stiffness of the muscles. With guidance from your medical provider, you can first care for the joint. Then when cleared, seeking help from a well-qualified fitness professional, you can improve joint health and ROM with corrective exercise.
Our Exercise Specialist has a lengthy background in functional fitness and mobility. Call us today to set up a consultation and start affordable training today.
1. Regular Adjustments: Schedule consistent chiropractic adjustments to keep your spine aligned and reduce any discomfort. 2. Posture Improvement: Focus on maintaining good posture, especially if you spend a lot of time sitting or using a computer. Consider using ergonomic furniture and taking breaks to move around. 3. Stretching & Exercise: Incorporate stretching and strengthening exercises into your routine to support your spine. Our exercise department can help you personalize a workout. 4. Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support bone health, like omega EFAs, a multivitamin, probiotics and vitamin D. 5. Stress Management: Practice stress-relief techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or hobbies you enjoy to reduce tension in your muscles. 6. Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your body hydrated and maintain the elasticity of spinal discs. 7. Sleep Well: Ensure you have a supportive mattress and pillow, and try to sleep in a position that keeps your spine aligned. 8. Educational Newsletter: Read our newsletters and blogs on our website for healthy living tips. 9. Regular Assessments: Have periodic assessments to track your progress and make necessary adjustments to your chiropractic care plan. 10. Positive Mindset: Stay positive and motivated. Celebrate small victories and stay committed to your health journey.
A baker's cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled sac that forms at the back of the knee joint. It is named after William Morrant Baker, an English surgeon who first described it in the 19th century. The cyst forms when the synovial fluid, which normally lubricates the knee joint, accumulates and bulges out towards the back of the knee. It is usually associated with underlying knee joint conditions such as arthritis, meniscal tears, or other inflammatory conditions. Baker's cysts are typically non-cancerous and may cause symptoms such as swelling, pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion in the knee joint. Treatment options for a baker's cyst include rest, medications to reduce inflammation, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical drainage or removal of the cyst.
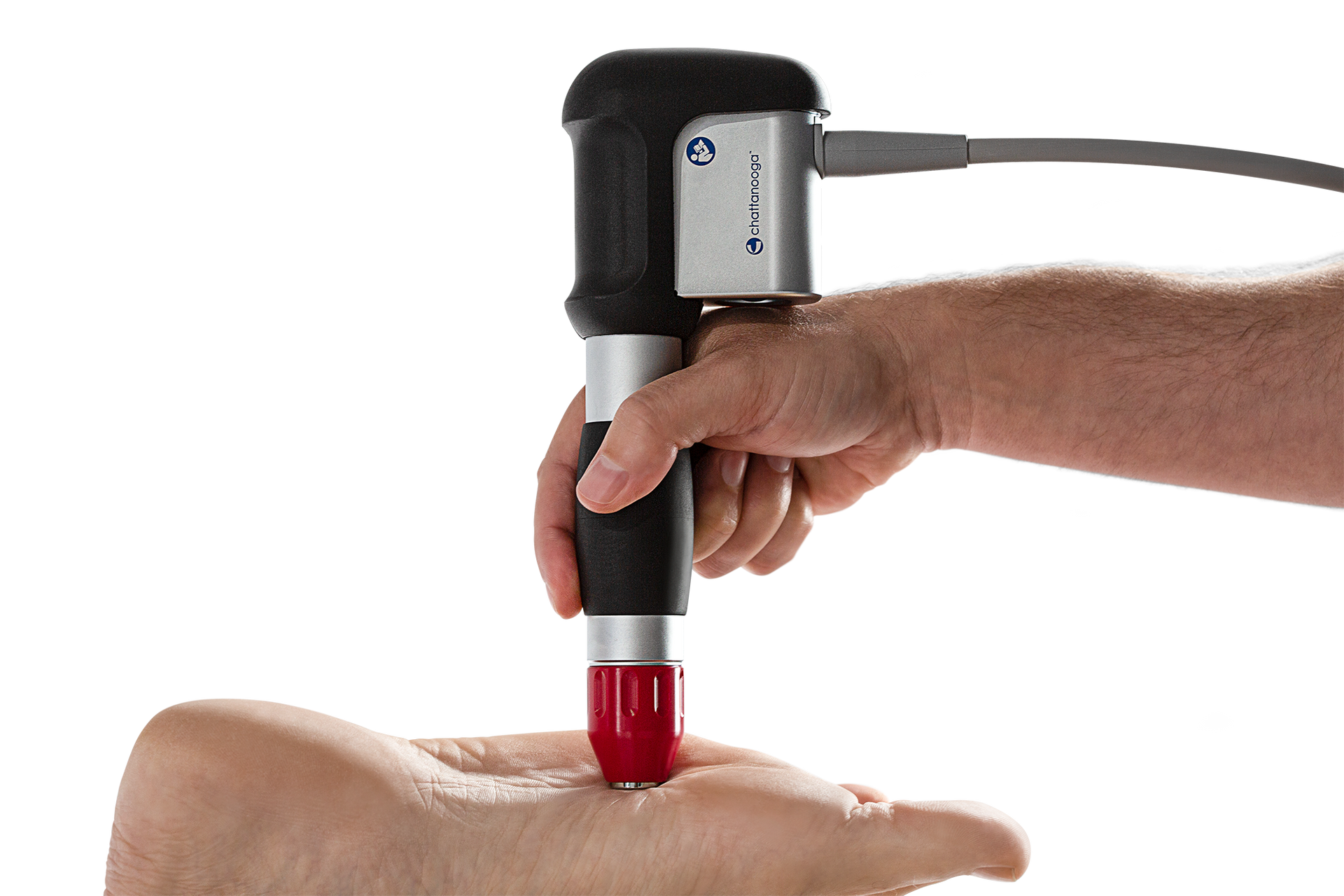

Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive medical treatment that uses high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate the healing process in various conditions. It is primarily used in the treatment of musculoskeletal conditions such as plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis, tennis elbow, and other similar injuries. During the therapy, a handheld device is used to deliver acoustic waves to the affected area. These waves create microtrauma in the tissue, promoting the release of growth factors and stimulating the body's natural healing response. This helps to improve blood circulation, reduce pain, and promote tissue regeneration. Shockwave therapy is usually conducted as a series of sessions, depending on the specific condition being treated. It is considered a safe and effective treatment option for many patients, although it may cause some discomfort during the procedure. Ask your chiropractor about Shockwave Therapy today!

According to the Association of Pickleball Professionals, almost 1 in 5 American adults have played pickleball in the last year. This is a 35% increase over the year before. With increasing popularity of the sport, let’s address some ways to prevent injuries and play safely. 1. Warm up. While you might be tempted to just step on the court and start playing, not allowing your body to warm up can increase injury risk. Aim for a 5-10 minute warm-up including light cardio movements and shoulder exercises. 2. Don’t overdo it. Gradually increase the amount of time you play with rest days between. 3. Do strength training exercises. Condition your body to tolerate increased load. This is especially important for the rotator cuff, core, and knees. 4. Don’t forget to protect your eyes. The pickleball can travels faster than a tennis ball since it is smaller. When there are quick battles at the kitchen line, there is a chance it could hit your face.

In honor of Breast Cancer Awareness Month, we want to bring awareness for the examination and detection of lumps in the breast tissue. Below are some tips to follow to start monthly checks at home! If you have any concerns, please mention them to your primary care provider. Monthly breast exams starting in the 20s Regular self-exams may make you more likely to catch any changes Review your self-exam technique with your doctor There are three different types of breast exams: Circular: Start at the outer edge of your breast and move fingers around the entire breast in a circular motion Vertical: Start at your underarm area and move your fingers downwards and back up until you have checked your entire breast Wedge: Start at the outer edge of your breast and move your fingers toward the nipple and back to the edge until you have checked the entire breast in small wedge-shaped sections Use the pads of your three middle fingers when performing exam Always check your underarm and upper chest wall Apply different levels of pressure Look at your breasts in a mirror to check for any changes such as, breast shape and/or swelling

When you care about your car, you take it to the shop for tune ups it needs—oil changes, tire rotations, new brakes, etc. Your spine is no different. It needs a regular “tune up” as well, complete with chiropractic adjustments. Chiropractic tune ups can serve three purposes: 1. Evaluate the state of your body, even if you have no pain. Even people who feel fine have areas of their spine or extremities that are out of normal alignment. When we adjust those bones back into place, people feel better in some way. If we waited until we felt pain, we would all wait until we needed root canals or crowns before going to the dentist! 2. Address major or minor pains you currently have, but have not been too worried about. Have you had any nagging discomforts or pain coming from your spine or your extremities? Do these discomforts prevent you from doing the activities you enjoy? Instead of wondering if the pain will continue to get worse or stay that way from the rest of your life, give chiropractic a try. You do not have to live with pain. 3. Prevent future problems that can and likely will arise from your joints being out of alignment and not functioning at 100%. Our society is moving toward preventative health care. Chiropractic has been at the forefront of this concept since the chiropractic profession was founded in 1895. Arthritis, overuse injuries (like carpal tunnel and tennis elbow), rotator cuff injuries, and knee problems are just some examples of conditions that may be prevented with chiropractic care. Scheduling chiropractic tune ups allow you take care of your body so that your machine functions as well as it possibly can. Please remember to make time to care for yourself; you are worth every penny.

Annual physical exams and wellness check-ups. Take this opportunity to discuss any concerns you may have and realize no question is too small when it comes to your wellbeing. Fuel your body with a well-balanced & colorful diet. Sticking to the outsides of the grocery store when shopping is a great place to start. Remember the longer the shelf life the less nutrients it has. Get active! It is recommended to get a minimum of 30 minutes of physical activity a day. Take breaks during your day to breathe and refocus. Stress is a major health concern when left unmanaged. Restful sleep. Women should be getting between 7-9 hours of sleep every night for optimal hormone function. Be mindful of how we are caring for ourselves, and May this month nudge you in the right direction.

1. Practice what you preach. It’s considerably easier to convince your children to adopt healthy habits if you’re doing the same. 2. Involve the whole family. Establishing a regular pattern of exercising as a family accomplishes two important things: It keeps everyone in shape and serves as important bonding time. 3. Limit screen time. Too much time watching television or playing video/computer games can lead to excessive snacking and a sedentary lifestyle. 4. Make it fun. Let your children discover which specific healthy activities they truly enjoy. If they don’t like it, they won’t stick with it. 5. Focus on the positives. Celebrate your children’s successes and help them develop a healthy self-image. Low self-esteem can lead to poor eating, exercise, and lifestyle habits. 6. Set goals and limits. If goals are excessively restrictive or vague, children are less likely to rise to the challenge. Establish clear nutrition and exercise goals (dessert two times a week; a half-hour walk five times a week, etc.). 7. Reward wisely . Rather than rewarding children with desserts or sugary snacks (a common tactic), find healthy ways to show a job well done. 8. Turn them into chefs. Get your children involved in planning and preparing meals; then sit down at the dinner table together and enjoy the healthy meal you’ve created together. 9. Knowledge is power. Teach children the value of reading food labels and being aware of the healthy (and not so healthy) ingredients in the foods they eat. 10. Don’t pass the buck. You’re the parent—that means it’s up to you to teach your children about good health. School and health care providers can only do so much.

“It’s too cold. I’ll get sick. I might slip and fall.” All common excuses for avoiding exercise when the seasons change. With four to six months of winter in many parts of the country, you can’t afford to skip winter exercise altogether. For both physical and mental well-being, the human body needs activity all year round. Whether you find creative ways to exercise indoors or dive into the great outdoors, maintaining an exercise regimen through the holidays and beyond not only keep you fit, but also give you a head start come spring. TAKE IT OUTSIDE If you don’t want to stay cooped up inside for months, exercising outdoors can be a great way to stay in shape while appreciating the sights and sounds of winter. From snowball fights and sledding to snowshoeing and cross-country skiing, a host of outdoor activities awaits you. Of course, if you have any medical conditions or concerns about outdoor exercise, check with your doctor first. Here are a few tips to help make the most of your time outdoors: • Dress for the cold • Protect your skin • Drink fluids • Beware of wind chill • Don’t push your luck in dangerous conditions STAY INDOORS Despite all the excuses for not wanting to face the elements, there are times when it is wise to avoid outdoor activities. If you find yourself in the mist of a polar vortex, try one of these indoor workout options: • Walk the mall • Hit the gym • Take a dip in an indoor pool • Create a home gym Winter can be one of the most exhilarating times of the year. With the sun and snow and a variety of winter sports to choose from, there’s no reason to hibernate indoors. It may be chilly and downright freezing at times, but your body still craves at least 30 minutes of exercise each day. Stay indoors if you have to, but if the conditions are decent and you dress appropriately, you can walk, run, hike, and play sports outside. Once you get going, you won’t even notice the cold.

Here are some tips to help minimize the chance that your back does not get injured while clearing the snow. 1. Stretch both before and after shoveling! You want to make sure your muscles are warmed up prior to shoveling as shoveling is both a cardio and weight training activity. This is especially true first thing in the morning when shoveling before work or getting the kids off to school. 2. Do not lift the snow. Lifting snow in the shovel can be a very heavy weight that you may not normally try to lift. Instead, push the snow forward and to the sides. In my house, we have a shovel that has a 48” blade that works great for pushing lighter, fluffy snow, but I would never use for the wet, heavy snow. 3. Do NOT twist and lift! Twisting or rotation puts extra stress on your discs and can lead to an even worse injury to your back than a simple low back strain. 4. Lift with your legs and not your back if you have to lift. Think of doing this similar to doing squats in the gym where you engage and support your low back and use the strength of your legs to lift. 5. Take lots of breaks. Shovel an area and then take a quick break to stretch before continuing to shovel. The likelihood of an injury happening is a lot lower and you likely won’t be sore later.
